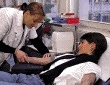
Recipient & TransfusionRationaleDetailed indications for the different blood components are documented in the "revue de l'agence française de sécurité sanitaire des produits de santé" (AFSSAPS). Transfusion thresholdLike any other medical treatment, the decision to give or not a blood transfusion to a patient is made after careful consideration. The risks of a transfusion should always be balanced with alternative treatments if available (e.g. erythropoietin for chronic anemia in chronic renal failure). Patient's blood tests (pre-transfusion testing)Prior to blood transfusion, or expected need for transfusion in surgery or transplantation, the patient is first tested for blood types and "subtypes". Pre-transfusion antibody screening of patients and/or cross-matching with donor's blood using very sensitive techniques should also be done to avoid severe hemolytic immunological transfusion reactions. These tests are routinely performed only prior to erythrocyte, but not platelet transfusion. Read more... TransfusionBefore transfusing, often a final ABO compatibility test is performed (the bedside test). This is not a compulsory test throughout the world, but rather widely practiced in countries such as France, Germany, some parts of Switzerland, etc... This test should avoid so-called "clerical errors" resulting in blood units being infused into the wrong patient. Blood components are infused through a tube connected to a needle inserted into a vein, usually in the arm. The amount and type of blood components transfused depend on the specific need of the patient. The patient is carefully monitored during and after transfusion. Apparition of any signs or symptoms suggesting a transfusion reaction are regularly checked. Vital signs (blood pressure, pulse, body temperature, ...) are evaluated at regular intervals during and for one hour after the transfusion. A red cell unit usually takes 1h30 to be transfused, but can be infused much more quickly, or more slowly especially in elderly patients. Platelets and plasma units are usually transfused in 20 to 30 minutes. |
|
|
Transplantation Immunology | |||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
 Print
Print