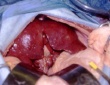
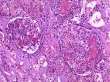
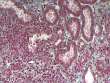
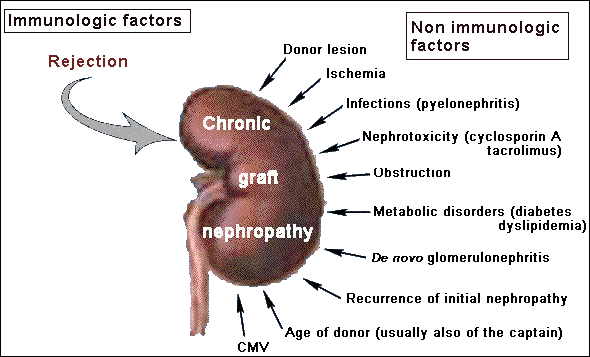
Three type of graft rejection: example of kidneyAccording to the time point of appearance and to the immune response, rejection are usually classified as: Hyperacute rejectionHyperacute rejection occurs when a vascularized organ suffers from rejection within minutes to hours (< 48 hours) after transplantation. This type of rejection is difficult to manage and needs high doses of immunosuppressive drugs, but often leads to graft loss. Hyperacute rejection is a complication more frequently encountered after transplantation of kidney. It is an humoral mechanism that is related to the presence of preformed antibodies anti-HLA or against incompatible blood group. Read more... Acute rejectionAcute rejection occurs during the first week and months after transplantation. Rejection is expected between two individuals who are not genetically identical (in major histocompatibility loci and minor histocompatible loci). To prevent rejection of the transplant, patient received immunosuppression drugs duringhis entire life. Nowadays, acute rejection occurs in 15 to 20% of the transplanted patients (kidney). The treatment of acute rejection is usually successfully performed by high dose of steroid and/or antibody therapy. Acute rejection is a cellular mechanism mediated by T cells and APC. Read more... Chronic rejectionThis term is used when allograft function slowly deteriorates and there is histologic evidence of vascular hypertrophy and fibrosis. Chronic rejection is nowadays the main source of complications and long term failure of kidney, heart, lung and pancreas transplantation, whereas chronic rejection is not a significant problem in liver transplantation. Chronic rejection is due different mechanisms including humoral and cellular mechanisms as well as a number of non immunological parameters related to transplant procurement, the operative procedure and various events post transplant which contribute to the intensity of chronic rejection. Read more... |
|
|
Transplantation Immunology | |||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
 Print
Print